Lab-grown meat, also known as cultured or cell-based meat, is revolutionizing the future of food production. This innovative technology involves growing meat directly from animal cells in a lab, without the need to raise and slaughter livestock. The promise of cultured meat goes beyond just providing a sustainable alternative to traditional meat—it holds the potential to reduce the environmental footprint of the food industry, improve animal welfare, and create more efficient methods of meat production.
As the demand for alternative proteins grows, lab-grown meat has caught the attention of startups, established food companies, and regulatory bodies. The technology is still in its early stages but has already made impressive strides, with a variety of companies around the world racing to bring these products to market.
In this blog, we will explore the global filing trends, patent landscape, market size, key players, and companies that are shaping this emerging industry.
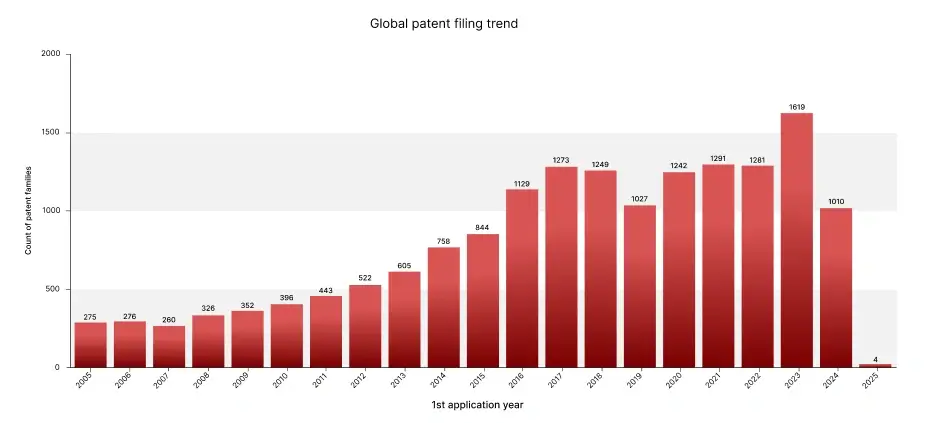
Discover key trends and innovations in the cultivated meat market with our patent landscape sample report. Gain valuable insights into emerging technologies, market leaders, and growth opportunities. Request your free sample report today and stay ahead of the competition in this rapidly evolving industry!
1 Cell Culture – This is the most common method utilized in cultured meat production. It entails separating animal cells (typically muscle or fat cells) and culturing them in a controlled setting, where they can grow and divide. The cells are supplemented with nutrients, growth factors, and other conditions that stimulate them to develop muscle tissue, just like they would in the body of an animal. This procedure generates small quantities of cultured meat that can be grown and harvested for food.
Some of the leading patents related to the cell culture cultivated meat production technique
2 3D Bioprinting – 3D bioprinting is a new technology that employs a printer to print layer by layer bio-inks with cells, growth factors, and scaffolding materials to create complex tissue structures. The method provides greater control over the texture, shape, and size of the cultured meat, replicating the natural composition of muscle and fat tissues of actual meat. This process has the potential to enhance the sensory attributes (such as taste and texture) of farm-grown meat.
Some of the leading patents related to the 3D Bioprinting technique
3 Scaffold-based Methods – Scaffold-based methods employ a structure, or scaffold, to guide the development and alignment of cells into the target tissue architecture. Scaffolds may be derived from natural or synthetic sources, which give mechanical support and assist cells in organizing themselves into muscle fibers. As cells proliferate, they form a bigger, cohesive piece of meat. Scaffolding assists in mimicking the natural structure and texture of meat, enhancing the final product’s mouthfeel and texture.
Some of the leading patents related to the Scaffold-based technique
Some of the leading patents related to the Bioreactor-based cultivation
5 Tissue Engineering – Tissue engineering involves marrying biological cells and engineering principles to cultivate tissues resembling natural muscle or fat. Tissue engineering involves cultivating muscle fibers and connective tissues in association with each other to form structures similar to meat. The procedure involves manipulating the cells to form desired shapes and structures, which may involve the use of scaffolds or bioreactors to promote the formation of the proper tissue. The aim of tissue engineering is to create meat that is very similar in texture and composition to normal meat.
Some of the leading patents related to the Tissue engineering
6 Synthetic Biology – Synthetic biology is a new discipline that uses engineering concepts in biology. Synbiotic biology in cultivated meat production involves genetic modification of cells so as to further them for meat production. For instance, scientists can change cells to enhance growth rates, increase fat content, or promote muscle development. This could potentially improve the efficiency and sustainability of the meat production process by allowing cells to grow more quickly or generate a more desirable balance of tissue.
US20220228121A1 – Cultured meat product with genetically modified cells
7 Microcarrier-based Cultivation – Here, animal cells are grown on tiny, round beads known as microcarriers. Microcarriers offer a surface for cell attachment and growth and enable high-density cell growth. This method is extensively employed in large bioreactors where the cells proliferate in suspension and microcarriers aid in the growth promotion of the cells and offer a 3D structure for the growth of tissues. This approach can enhance scalability and economic efficiency in cultivated meat production.
The global cultured meat market is estimated at ~ USD 250 million in 2023 and is projected to reach ~ USD 1.5 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of ~30% from 2023 to 2030.
Key Player Segmentation
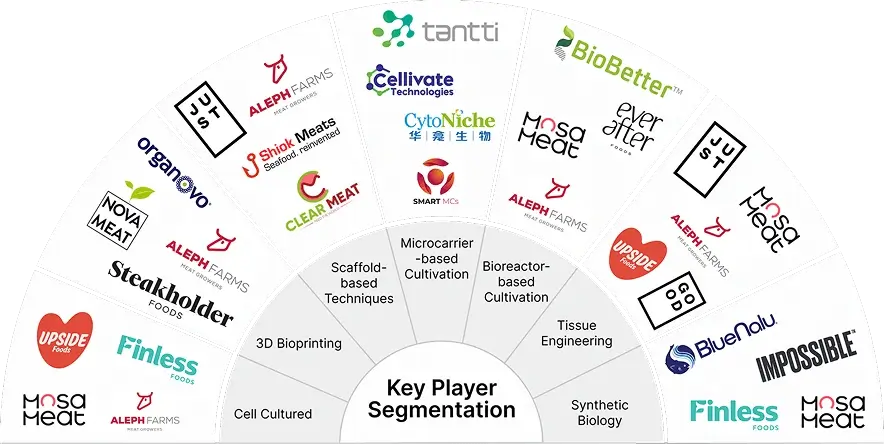
Cultured meat is a promising domain with potential to reach ~ USD 1.5 billion market evaluation growing at a CAGR of ~ 30% from 2023 to 2030. This article is just an overview about what’s happening in the domain right now for in-depth insights you can get in touch with our subject matter experts today.
For more than a decade, we have been offering top notch intellectual property (IP), technology, and market research service to our global clients, including Fortune 500 companies, small enterprises, and onshore IP law firms.
Services:
Schedule a one-on-one meeting with our subject matter experts and discuss your project queries today!

Reverse Engineering (RE) of Printed Circuit Board to Detect Patent Infringement

Versatile Video Coding (VVC): The Frontier Ahead of High-Efficiency Video Streaming and Compression Innovation

IPR in the Music Industry: Safeguarding Innovation in the Digital Music Era

Innovation in Automobile Industry: Key Tech & IP Trends to Watch
