Close

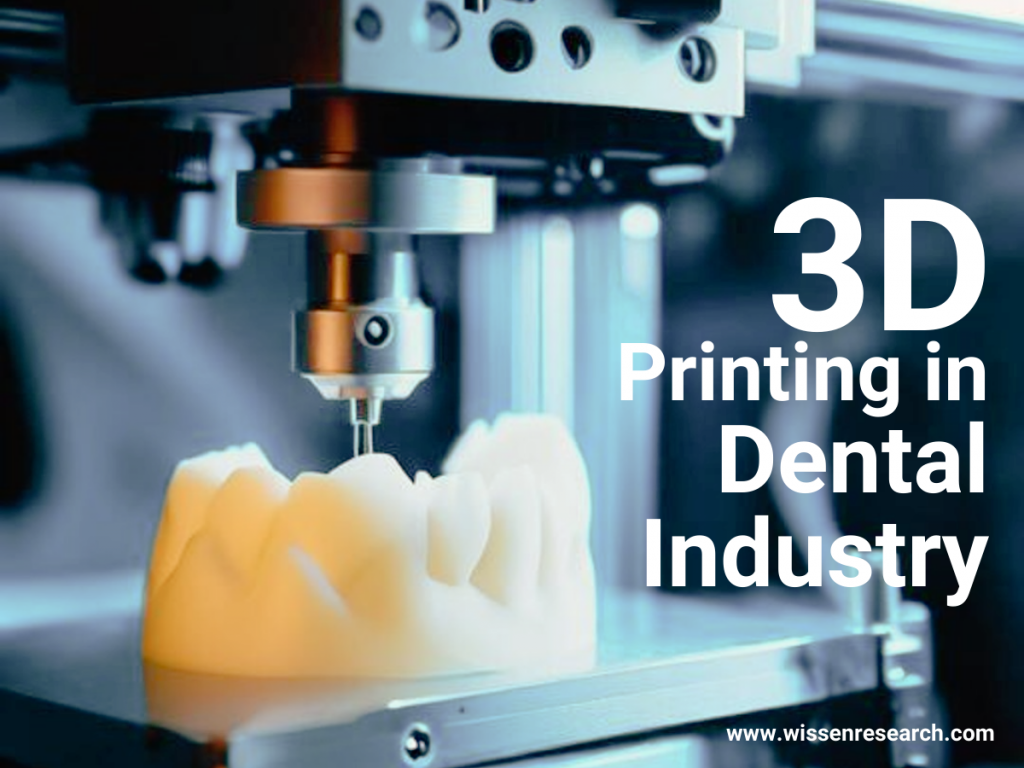
3D printing, also referred to as Additive Manufacturing, is a process for building three-dimensional things layer by layer using computer-aided design.
Since the first 3D printing technology was introduced in 1986, a wide range of industries have adopted the most advanced techniques, with additive manufacturing demonstrating enormous expansion. Dentistry is one of the industries that has adopted 3D printing extensively and quickly.
The dental industry and its technologies are continually evolving and changing, and with this, dentists are increasingly incorporating 3D printing in their workflow.
The Dental 3D Printing Market is anticipated to grow at a strong CAGR of 22.8% from 2022 to 2028, from USD 2.1 billion in 2021 to USD 8.84 billion in 2028.
By using additive manufacturing, dental 3D printing can produce dental components like crowns, dentures, and aligners. Dental professionals use a device called an intraoral scanner to produce custom parts that are tailored to a patient’s anatomy. This creates dental images of the patient and stores them as Computer-Aided Design (CAD) files. This CAD file is then used by dentists to 3D print dental moulds or implants. Dental implant and mould production used to be a time-consuming, invasive, and at times uncomfortable procedure. The process of treating patients has been greatly sped up and simplified by 3D printing.
What are the Applications of Dental 3D Printing?

The following are some of the most common applications of 3D printing in dentistry:
The production of dental products using traditional methods has several drawbacks, including expensive and inaccurate dental products, lengthy printing procedures, and low-quality printing.
Dental 3D printing expands treatment options for both patients and doctors at affordable costs, improving the standard of patient care and services. Additionally, because this is a digitalized process, the goods produced using it may be easily customized (even complex dental structures), providing more exact and accurate solutions for dental applications.


The integration of 3D printing technology in the dental industry has brought about remarkable advancements in precision, speed, treatment planning, education, and material options. By harnessing the power of 3D printing, dental professionals are delivering more personalized, efficient, and effective care to their patients, ultimately transforming the landscape of modern dentistry.
Authored by – Guniyal Bagga
Please Subscribe our news letter and get update.
© Copyright 2023 – Wissen Research All Rights Reserved.
Powered by VintageCoders