Close


Trademarks play a pivotal role in establishing brand identity, trust, and consumer recognition. When businesses decide to license their trademarks to third parties, they often do so to extend their brand reach and generate additional revenue. However, the concept of “naked licenses” can have potentially detrimental consequences. A naked license occurs when a trademark owner licenses their mark to a third party without sufficient quality control or supervision. This article explores the risks and implications of naked licenses of trademarks to unmonitored licensees.
A trademark license is an agreement that permits a third party (the licensee) to use the trademark of the licensor for specific goods or services. Trademark owners enter into licensing agreements for various reasons, including franchising, distribution, and brand expansion. These licenses can take different forms, such as exclusive or non-exclusive licenses. However, when a trademark owner grants a license without imposing adequate quality control measures or monitoring the licensee’s activities, it becomes a “naked license.”
Naked licenses can have several adverse effects on a trademark’s legal standing and brand reputation:

1. Abandonment of Trademark Rights: One of the most significant risks associated with naked licenses is the potential abandonment of trademark rights. Under U.S. trademark law, a trademark owner must actively control the quality of the goods or services provided by the licensee. Failure to exercise this control can lead to the loss of trademark rights. This means that the trademark owner may no longer be able to prevent others from using the same or similar mark.
Trademark searches and monitoring maintain distinctiveness but won’t prevent abandonment from poor quality control by licensees; they mainly watch for infringements.
https://www.wissenresearch.com/trademark-search/
https://www.wissenresearch.com/trademark-monitoring/
https://www.wissenresearch.com/contract-lifecycle-management/
2. Diminished Brand Reputation: When a licensee operates without proper oversight, the quality of the goods or services may not meet the standards associated with the trademark. Poor quality or negative customer experiences can result in a tarnished brand reputation. Customers who encounter subpar products or services may associate the trademark with low quality, which can be challenging to overcome.
Search services protect your brand from infringements but can’t stop a tarnished reputation due to poor licensee quality; that needs direct owner oversight.
https://www.wissenresearch.com/trademark-search/
https://www.wissenresearch.com/trademark-monitoring/
https://www.wissenresearch.com/contract-lifecycle-management/
3. Infringement Risks: Unmonitored licensees may engage in activities that infringe on the rights of others. This can lead to trademark infringement lawsuits that could implicate the trademark owner as a contributory infringer, especially if they were aware of the licensee’s infringing activities and did nothing to prevent them.
Search services like Trademark Clearinghouse, TMview, and USPTO’s TESS detect trademark use but don’t stop licensee infringement. Owner oversight is crucial to avoid legal trouble.
https://www.wissenresearch.com/trademark-search/
https://www.wissenresearch.com/trademark-monitoring/
https://www.wissenresearch.com/contract-lifecycle-management/
4.Weakening of Distinctiveness: Trademarks rely on their distinctiveness to provide legal protection. When a trademark is associated with a wide range of goods or services offered by unmonitored licensees, its distinctiveness can be diluted, making it more challenging to enforce trademark rights against potential infringers.
Search services monitor trademark use but won’t prevent licensee actions that weaken distinctiveness. Active control by owners is key to maintaining trademark strength.
https://www.wissenresearch.com/trademark-search/
https://www.wissenresearch.com/trademark-monitoring/
https://www.wissenresearch.com/contract-lifecycle-management/
To avoid the risks associated with naked licenses, trademark owners should take the following steps:
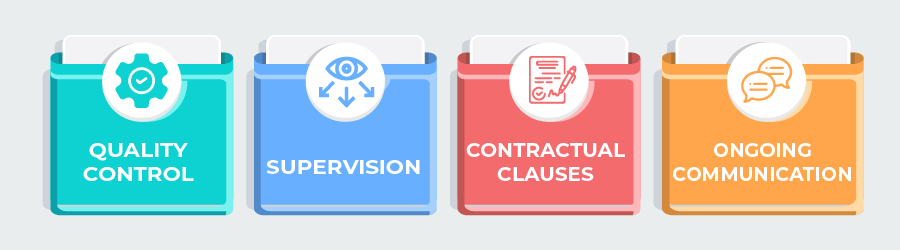
Naked licenses of trademarks to unmonitored licensees carry significant risks that can harm a brand’s reputation and result in the loss of valuable trademark rights. To protect their trademarks and maintain the integrity of their brands, trademark owners should be diligent in implementing quality control measures, monitoring their licensees, and maintaining clear lines of communication. By taking these steps, businesses can ensure that their trademarks continue to symbolize quality and reliability in the eyes of consumers while extending their brand presence through responsible licensing.
Authored by – Nitesh Chouhan
Edited by : Guniyal
Please Subscribe our news letter and get update.
© Copyright 2023 – Wissen Research All Rights Reserved.
Powered by VintageCoders